Building a Marketplace for Data Mesh: Domain Data Catalogs – Part 3
Actian Corporation
June 10, 2024

Over the past decade, data catalogs have emerged as important pillars in the landscape of data-driven initiatives. However, many vendors on the market fall short of expectations with lengthy timelines, complex and costly projects, bureaucratic data governance models, poor user adoption rates, and low-value creation. This discrepancy extends beyond metadata management projects, reflecting a broader failure at the data management level.
Given these shortcomings, a new concept is gaining popularity: the internal marketplace, or what we call the Enterprise Data Marketplace (EDM).
In this series of articles, get an excerpt from our Practical Guide to Data Mesh where we explain the value of internal data marketplaces for data product production and consumption, how an EDM supports data mesh exploitation on a larger scale, and how they go hand-in-hand with a data catalog solution:
- Facilitating data product consumption through metadata.
- Setting up an enterprise-level marketplace.
- Feeding the marketplace via domain-specific data catalogs.
Structuring data management around domains and data products is an organizational transformation that does not change the operational reality of most organizations: data is available in large quantities, from numerous sources, evolves rapidly, and its control is complex.
Data catalogs traditionally serve to inventory all available data and manage a set of metadata to ensure control and establish governance practices.
Data mesh does not eliminate this complexity: it allows certain data, managed as data products, to be distinguished and intended for sharing and use beyond the domain to which they belong. But each domain is also responsible for managing its internal data, which will be used to develop robust and high-value data products – its proprietary data, in other words.
Metadata Management in the Context of an Internal Marketplace fed by Domain-Specific Catalogs
In the data mesh, the need for a Data Catalog does not disappear, quite the contrary: each domain should have a catalog allowing it to efficiently manage its proprietary data, support domain governance, and accelerate the development of robust and high-value data products. Metadata management is thus done at two levels:
- At the domain level – in the form of a catalog allowing the documentation and organization of the domain’s data universe. Since the Data Catalog is a proprietary component, it is not necessary for all domains to use the same solution.
- At the mesh level – in the form of a marketplace in which the data products shared by all domains are registered; the marketplace is naturally common to all domains.
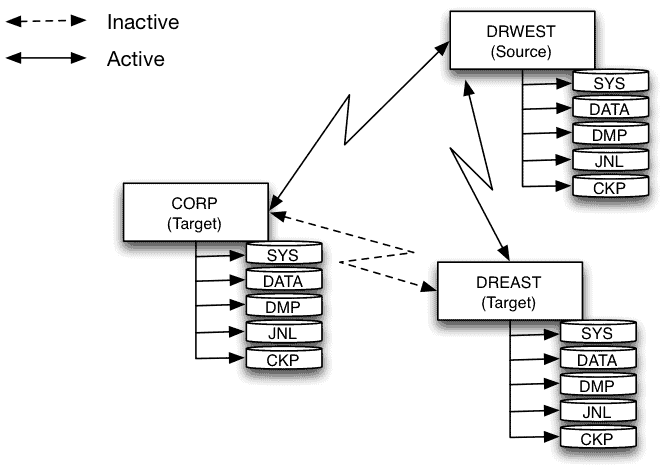
With a dedicated marketplace component, the general architecture for metadata management is as follows:
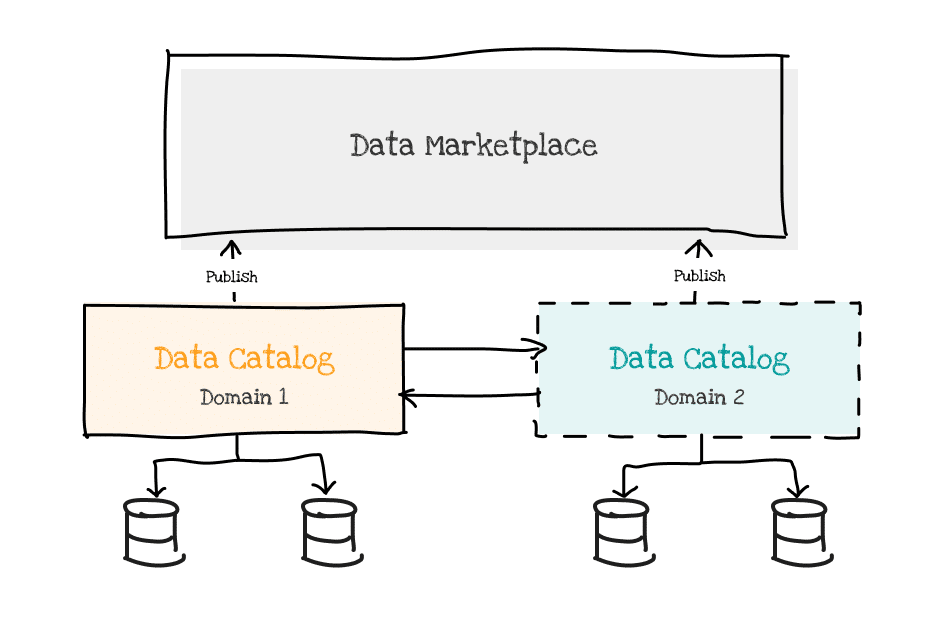
In this architecture, each domain has its own catalog – which may rely on a single solution or not – but should be instantiated for each domain to allow it to organize its data most effectively and avoid the pitfalls of a universal metadata organization.
The marketplace is a dedicated component, offering simplified ergonomics, and in which each domain deploys metadata (or even data) for its data products. This approach requires close integration of the different modules:
- Domain catalogs must be integrated with the marketplace to avoid duplicating efforts in producing certain metadata – especially lineage, but also data dictionaries (schema), or even business definitions that will be present in both systems.
- Domain catalogs potentially need to be integrated with each other – to share/synchronize certain information, primarily the business glossary but also some repositories.
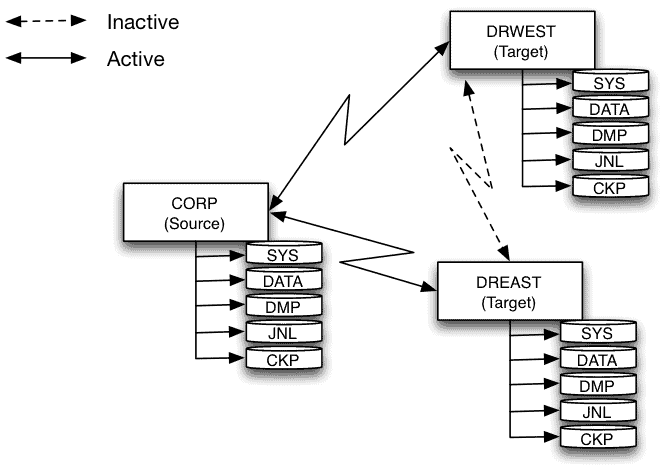
Data Catalog vs. EDM Capabilities
When we look at the respective capabilities of an Enterprise Data Marketplace and a Data Catalog, we realize that these capabilities are very similar:
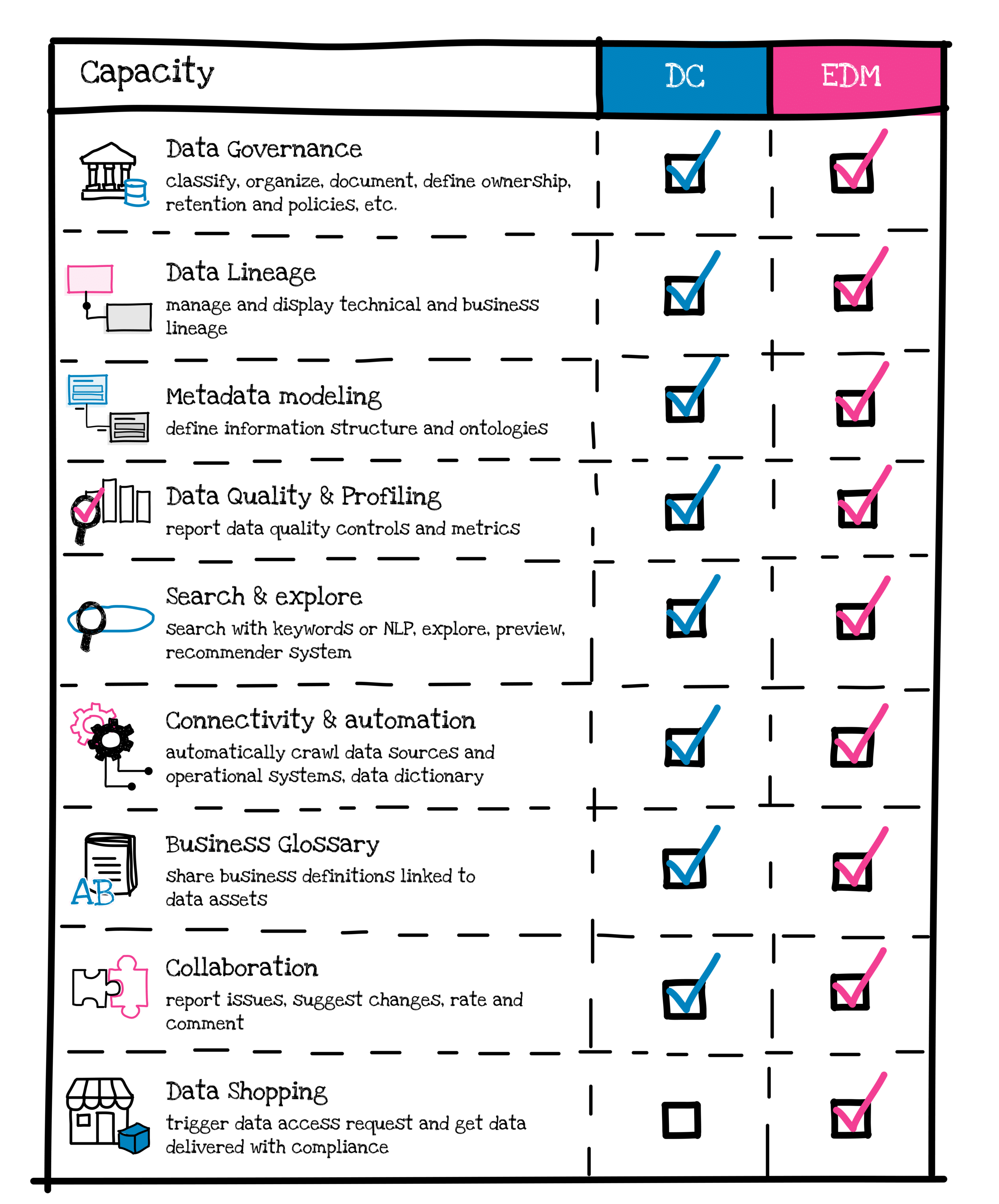
In the end, on a strictly functional level, their capabilities are very similar. What distinguishes a modern Data Catalog from an EDM are:
- Their scope – The Data Catalog is intended to cover all data, whereas the marketplace is limited to the objects shared by domains (data products and other domain analytics products).
- Their user experience – The Data Catalog is often a fairly complex tool, designed to support governance processes globally – it focuses on data stewardship workflows. The marketplace, on the other hand, typically offers very simple ergonomics, heavily inspired by that of an e-commerce platform, and provides an experience centered on consumption – data shopping.
The Practical Guide to Data Mesh: Setting up and Supervising an Enterprise-Wide Data Mesh
Written by Guillaume Bodet, our guide was designed to arm you with practical strategies for implementing data mesh in your organization, helping you:
- Start your data mesh journey with a focused pilot project.
- Discover efficient methods for scaling up your data mesh.
- Acknowledge the pivotal role an internal marketplace plays in facilitating the effective consumption of data products.
- Learn how the Actian Data Intelligence Platform emerges as a robust supervision system, orchestrating an enterprise-wide data mesh.
Subscribe to the Actian Blog
Subscribe to Actian’s blog to get data insights delivered right to you.
- Stay in the know – Get the latest in data analytics pushed directly to your inbox.
- Never miss a post – You’ll receive automatic email updates to let you know when new posts are live.
- It’s all up to you – Change your delivery preferences to suit your needs.
Subscribe
(i.e. sales@..., support@...)