Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of Data Warehousing
What is a Data Warehouse?
The Business Imperative of Data Warehousing
The Technical Role of Data Warehousing
Understanding the Differences: Databases, Data Warehouses, and Analytics Databases
The Human Side of Data: Key User Personas and Their Pain Points
Data Warehouse Use Cases For Modern Organizations
6 Common Business Use Cases
9 Technical Use Cases
Understanding the Basics of Data Warehousing
Welcome to data warehousing 101. For those of you who remember when “cloud” only meant rain and “big data” was just a database that ate too much, buckle up—we’ve come a long way. Here’s an overview:
What is a Data Warehouse?
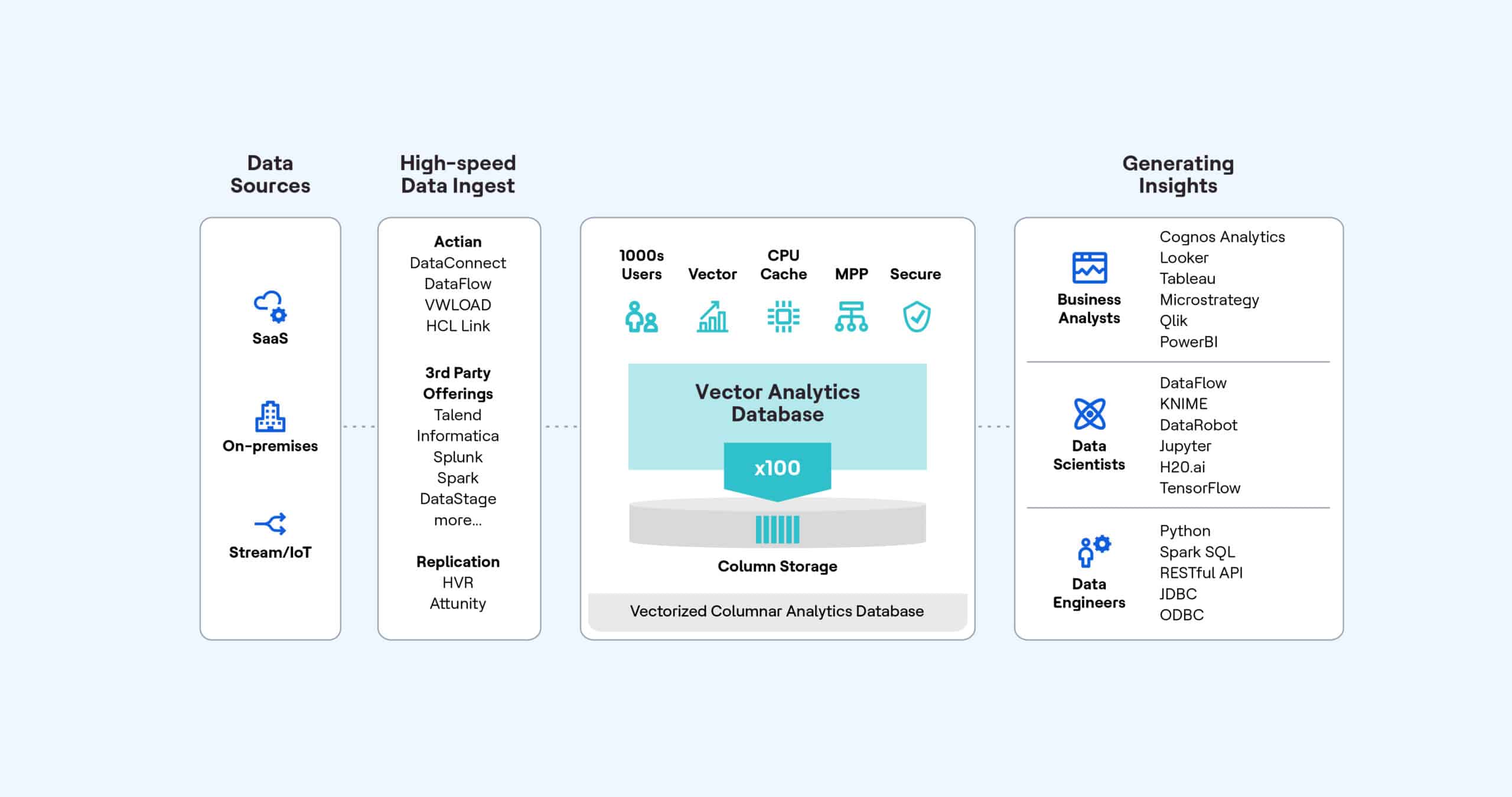
Data warehouses are large storage systems where data from various sources is collected, integrated, and stored for later analysis. Data warehouses are typically used in business intelligence (BI) and reporting scenarios where you need to analyze large amounts of historical and real-time data. They can be deployed on-premises, on a cloud (private or public), or in a hybrid manner.
Think of a data warehouse as the Swiss Army knife of the data world – it’s got everything you need, but unlike that dusty tool in your drawer, you’ll actually use it every day!
Prominent examples include Actian Data Platform, Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Snowflake, Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics, and IBM Db2 Warehouse, among others.
Proper data consolidation, integration, and seamless connectivity with BI tools are crucial for a data strategy and visibility into the business. A data warehouse without this holistic view provides an incomplete narrative, limiting the potential insights that can be drawn from the data.
“Proper data consolidation, integration, and seamless connectivity with BI tools are crucial aspects of a data strategy. A data warehouse without this holistic view provides an incomplete narrative, limiting the potential insights that can be drawn from the data.”
The Business Imperative of Data Warehousing
Data warehouses are instrumental in enabling organizations to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently. The primary value of a data warehouse lies in its ability to facilitate a comprehensive view of an organization’s data landscape, supporting strategic business functions such as real-time decision-making, customer behavior analysis, and long-term planning.
But why is a data warehouse so crucial for modern businesses? Let’s dive in.
A data warehouse is a strategic layer that is essential for any organization looking to maintain competitiveness in a data-driven world. The ability to act quickly on analyzed data translates to improved operational efficiencies, better customer relationships, and enhanced profitability.
The Technical Role of Data Warehousing
The primary function of a data warehouse is to facilitate analytics, not to perform analytics itself. The BI team configures the data warehouse to align with its analytical needs. Essentially, a data warehouse acts as a structured repository, comprising tables of rows and columns of carefully curated and frequently updated data assets. These assets feed BI applications that drive analytics.
“The primary function of a data warehouse is to facilitate analytics, not to perform analytics itself.”
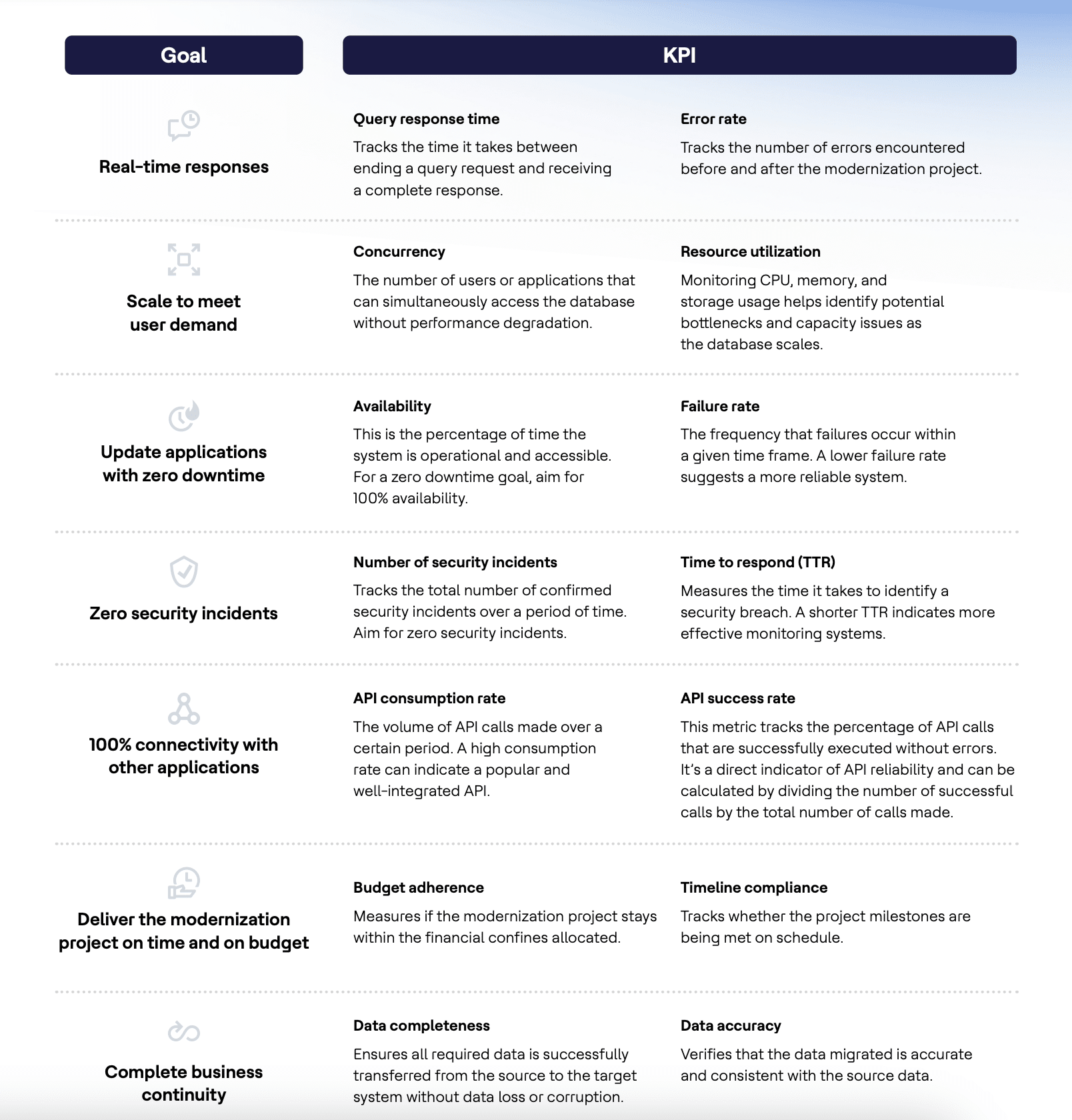
Achieving the business imperatives of data warehousing relies heavily on these four key technical capabilities:
1. Real-Time Data Processing: This is critical for applications that require immediate action, such as fraud detection systems, real-time customer interaction management, and dynamic pricing strategies. Real-time data processing in a data warehouse is like a barista making your coffee to order–it happens right when you need it, tailored to your specific requirements.
2. Scalability and Performance: Modern data warehouses must handle large datasets and support complex queries efficiently. This capability is particularly vital in industries such as retail, finance, and telecommunications, where the ability to scale according to demand is necessary for maintaining operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
3. Data Quality and Accessibility: The quality of insights directly correlates with the quality of data ingested and stored in the data warehouse. Ensuring data is accurate, clean, and easily accessible is paramount for effective analysis and reporting. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider the entire data chain when crafting a data strategy, rather than viewing the warehouse in isolation.
4. Advanced Capabilities: Modern data warehouses are evolving to meet new challenges and opportunities:
-
-
- Data Virtualization: Allowing queries across multiple data sources without physical data movement.
- Integration With Data Lakes: Enabling analysis of both structured and unstructured data.
- In-Warehouse Machine Learning: Supporting the entire ML lifecycle, from model training to deployment, directly within the warehouse environment.
“In the world of data warehousing, scalability isn’t just about handling more data—it’s about adapting to the ever-changing landscape of business needs.”
Understanding the Differences: Databases, Data Warehouses, and Analytics Databases
Databases, data warehouses, and analytics databases serve distinct purposes in the realm of data management, with each optimized for specific use cases and functionalities.
A database is a software system designed to efficiently store, manage, and retrieve structured data. It is optimized for Online Transaction Processing (OLTP), excelling at handling numerous small, discrete transactions that support day-to-day operations. Examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. While databases are adept at storing and retrieving data, they are not specifically designed for complex analytical querying and reporting.
Data warehouses, on the other hand, are specialized databases designed to store and manage large volumes of structured, historical data from multiple sources. They are optimized for analytical processing, supporting complex queries, aggregations, and reporting. Data warehouses are designed for Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), using techniques like dimensional modeling and star schemas to facilitate complex queries across large datasets. Data warehouses transform and integrate data from various operational systems into a unified, consistent format for analysis. Examples include Actian Data Platform, Amazon Redshift, Snowflake, and Google BigQuery.
Analytics databases, also known as analytical databases, are a subset of databases optimized specifically for analytical processing. They offer advanced features and capabilities for querying and analyzing large datasets, making them well-suited for business intelligence, data mining, and decision support. Analytics databases bridge the gap between traditional databases and data warehouses, offering features like columnar storage to accelerate analytical queries while maintaining some transactional capabilities. Examples include Actian Vector, Exasol, and Vertica. While analytics databases share similarities with traditional databases, they are specialized for analytical workloads and may incorporate features commonly associated with data warehouses, such as columnar storage and parallel processing.
“In the data management spectrum, databases, data warehouses, and analytics databases each play distinct roles. While all data warehouses are databases, not all databases are data warehouses. Data warehouses are specifically tailored for analytical use cases. Analytics databases bridge the gap, but aren’t necessarily full-fledged data warehouses, which often encompass additional components and functionalities beyond pure analytical processing.”
The Human Side of Data: Key User Personas and Their Pain Points
Welcome to Data Warehouse Personalities 101. No Myers-Briggs here—just SQL, Python, and a dash of data-induced delirium. Let’s see who’s who in this digital zoo.
Note: While these roles are presented distinctly, in practice they often overlap or merge, especially in organizations of varying sizes and across different industries. The following personas are illustrative, designed to highlight the diverse perspectives and challenges related to data warehousing across common roles.
- DBAs are responsible for the technical maintenance, security, performance, and reliability of data warehouses. “As a DBA, I need to ensure our data warehouse operates efficiently and securely, with minimal downtime, so that it consistently supports high-volume data transactions and accessibility for authorized users.”
- Data analysts specialize in processing and analyzing data to extract insights, supporting decision-making and strategic planning. “As a data analyst, I need robust data extraction and query capabilities from our data warehouse, so I can analyze large datasets accurately and swiftly to provide timely insights to our decision-makers.”
- BI analysts focus on creating visualizations, reports, and dashboards from data to directly support business intelligence activities. “As a BI analyst, I need a data warehouse that integrates seamlessly with BI tools to facilitate real-time reporting and actionable business insights.”
- Data engineers manage the technical infrastructure and architecture that supports the flow of data into and out of the data warehouse. “As a data engineer, I need to build and maintain a scalable and efficient pipeline that ensures clean, well-structured data is consistently available for analysis and reporting.”
- Data scientists use advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and predictive modeling, to create algorithms that predict future trends and behaviors. “As a data scientist, I need the data warehouse to handle complex data workloads and provide the computational power necessary to develop, train, and deploy sophisticated models.”
- Compliance officers ensure that data management practices comply with regulatory requirements and company policies. “As a compliance officer, I need the data warehouse to enforce data governance practices that secure sensitive information and maintain audit trails for compliance reporting.”
- IT managers oversee the IT infrastructure and ensure that technological resources meet the strategic needs of the organization. “As an IT manager, I need a data warehouse that can scale resources efficiently to meet fluctuating demands without overspending on infrastructure.”
- Risk managers focus on identifying, managing, and mitigating risks related to data security and operational continuity. “As a risk manager, I need robust disaster recovery capabilities in the data warehouse to protect critical data and ensure it is recoverable in the event of a disaster.”
Data Warehouse Use Cases For Modern Organizations
In this section, we’ll feature common use cases for both the business and IT sides of the organization.
6 Common Business Use Cases
This section highlights how data warehouses directly support critical business objectives and strategies.
1. Supply Chain and Inventory Management: Enhances supply chain visibility and inventory control by analyzing procurement, storage, and distribution data. Think of it as giving your supply chain a pair of X-ray glasses—suddenly, you can see through all the noise and spot exactly where that missing shipment of left-handed widgets went.
Examples:
-
-
-
- Retail: Optimizing stock levels and reorder points based on sales forecasts and seasonal trends to minimize stockouts and overstock situations.
- Manufacturing: Tracking component supplies and production schedules to ensure timely order fulfillment and reduce manufacturing delays.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring drug safety and availability by monitoring supply chains for potential disruptions and managing inventory efficiently.
2. Customer 360 Analytics: Enables a comprehensive view of customer interactions across multiple touchpoints, providing insights into customer behavior, preferences, and loyalty.
Examples:
-
-
-
- Retail: Analyzing purchase history, online and in-store interactions, and customer service records to tailor marketing strategies and enhance customer experience (CX).
- Banking: Integrating data from branches, online banking, and mobile apps to create personalized banking services and improve customer retention.
- Telecommunications: Leveraging usage data, service interaction history, and customer feedback to optimize service offerings and improve customer satisfaction.
3. Operational Efficiency: Improves the efficiency of operations by analyzing workflows, resource allocations, and production outputs to identify bottlenecks and optimize processes. It’s the business equivalent of finding the perfect traffic route to work—except instead of avoiding road construction, you’re sidestepping inefficiencies and roadblocks to productivity.
Examples:
-
-
-
- Manufacturing: Monitoring production lines and supply chain data to reduce downtime and improve production rates.
- Healthcare: Streamlining patient flow from registration to discharge to enhance patient care and optimize resource utilization.
- Logistics: Analyzing route efficiency and warehouse operations to reduce delivery times and lower operational costs.
4. Financial Performance Analysis: Offers insights into financial health through revenue, expense, and profitability analysis, helping companies make informed financial decisions.
Examples:
-
-
-
- Finance: Tracking and analyzing investment performance across different portfolios to adjust strategies according to market conditions.
- Real Estate: Evaluating property investment returns and operating costs to guide future investments and development strategies.
- Retail: Assessing the profitability of different store locations and product lines to optimize inventory and pricing strategies.
5. Risk Management and Compliance: Helps organizations manage risk and ensure compliance with regulations by analyzing transaction data and audit trails. It’s like having a super-powered compliance officer who can spot a regulatory red flag faster than you can say “GDPR.”
Examples:
-
-
-
- Banking: Detecting patterns indicative of fraudulent activity and ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering laws.
- Healthcare: Monitoring for compliance with healthcare standards and regulations, such as HIPAA, by analyzing patient data handling and privacy measures.
- Energy: Assessing and managing risks related to energy production and distribution, including compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
6. Market and Sales Analysis: Analyzes market trends and sales data to inform strategic decisions about product development, marketing, and sales strategies.
Examples:
-
-
-
- eCommerce: Tracking online customer behavior and sales trends to adjust marketing campaigns and product offerings in real time.
- Automotive: Analyzing regional sales data and customer preferences to inform marketing efforts and align production with demand.
- Entertainment: Evaluating the performance of media content across different platforms to guide future production and marketing investments.
These use cases demonstrate how data warehouses have become the backbone of data-driven decision making for organizations. They’ve evolved from mere data repositories into critical business tools.
In an era where data is often called “the new oil,” data warehouses serve as the refineries, turning that raw resource into high-octane business fuel. The real power of data warehouses lies in their ability to transform vast amounts of data into actionable insights, driving strategic decisions across all levels of an organization.
9 Technical Use Cases
Ever wonder how boardroom strategies transform into digital reality? This section pulls back the curtain on the technical wizardry of data warehousing. We’ll explore nine use cases that showcase how data warehouse technologies turn business visions into actionable insights and competitive advantages. From powering machine learning models to ensuring regulatory compliance, let’s dive into the engine room of modern data-driven decision making.
1. Data Science and Machine Learning: Data warehouses can store and process large datasets used for machine learning models and statistical analysis, providing the computational power needed for data scientists to train and deploy models.
Key features:
-
-
-
- Built-in support for machine learning algorithms and libraries (like TensorFlow).
- High-performance data processing capabilities for handling large datasets (like Apache Spark).
- Tools for deploying and monitoring machine learning models (like MLflow).
2. Data as a Service (DaaS): Companies can use cloud data warehouses to offer cleaned and curated data to external clients or internal departments, supporting various use cases across industries.
Key features:
-
-
-
- Robust data integration and transformation capabilities that ensure data accuracy and usability (using tools like Actian DataConnect, Actian Data Platform for data integration, and Talend).
- Multi-tenancy and secure data isolation to manage data access (features like those in Amazon Redshift).
- APIs for seamless data access and integration with other applications (such as RESTful APIs).
- Built-in data sharing tools (features like those in Snowflake).
3. Regulatory Compliance and Reporting: Many organizations use cloud data warehouses to meet compliance requirements by storing and managing access to sensitive data in a secure, auditable manner. It’s like having a digital paper trail that would make even the most meticulous auditor smile. No more drowning in file cabinets!
Key features:
-
-
-
- Encryption of data at rest and in transit (technologies like AES encryption).
- Comprehensive audit trails and role-based access control (features like those available in Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse).
- Adherence to global compliance standards like GDPR and HIPAA (using compliance frameworks such as those provided by Microsoft Azure).
4. Administration and Observability: Facilitates the management of data warehouse platforms and enhances visibility into system operations and performance. Consider it your data warehouse’s health monitor—keeping tabs on its vital signs so you can diagnose issues before they become critical.
Key features:
-
-
-
- A platform observability dashboard to monitor and manage resources, performance, and costs (as seen in Actian Data Platform, or Google Cloud’s operations suite).
- Comprehensive user access controls to ensure data security and appropriate access (features seen in Microsoft SQL Server).
- Real-time monitoring dashboards for live tracking of system performance (like Grafana).
- Log aggregation and analysis tools to streamline troubleshooting and maintenance (implemented with tools like ELK Stack).
5. Seasonal Demand Scaling: The ability to scale resources up or down based on demand makes cloud data warehouses ideal for industries with seasonal fluctuations, allowing them to handle peak data loads without permanent investments in hardware. It’s like having a magical warehouse that expands during the holiday rush and shrinks during the slow season. No more paying for empty shelf space!
Key features:
-
-
-
- Semi-automatic or fully automatic resource allocation for handling variable workloads (like Actian Data Platform’s scaling and Schedules feature, or Google BigQuery’s automatic scaling).
- Cloud-based scalability options that provide elasticity and cost efficiency (as seen in AWS Redshift).
- Distributed architecture that allows horizontal scaling (such as Apache Hadoop).
6. Enhanced Performance and Lower Costs: Modern data warehouses are engineered to provide superior performance in data processing and analytics, while simultaneously reducing the costs associated with data management and operations. Imagine a race car that not only goes faster but also uses less fuel. That’s what we’re talking about here—speed and efficiency in perfect harmony.
Key features:
-
-
-
- Advanced query optimizers that adjust query execution strategies based on data size and complexity (like Oracle’s Query Optimizer).
- In-memory processing to accelerate data access and analysis (such as SAP HANA).
- Caching mechanisms to reduce load times for frequently accessed data (implemented in systems like Redis).
- Data compression mechanisms to reduce the storage footprint of data, which not only saves on storage costs but also improves query performance by minimizing the amount of data that needs to be read from disk (like the advanced compression techniques in Amazon Redshift).
7. Disaster Recovery: Cloud data warehouses often feature built-in redundancy and backup capabilities, ensuring data is secure and recoverable in the event of a disaster. Think of it as your data’s insurance policy—when disaster strikes, you’re not left empty-handed.
Key features:
-
-
-
- Redundancy and data replication across geographically dispersed data centers (like those offered by IBM Db2 Warehouse).
- Automated backup processes and quick data restoration capabilities (like the features in Snowflake).
- High availability configurations to minimize downtime (such as VMware’s HA solutions).
Note: The following use cases are typically driven by separate solutions, but are core to an organization’s warehousing strategy.
8. (Depends on) Data Consolidation and Integration: By consolidating data from diverse sources like CRM and ERP systems into a unified repository, data warehouses facilitate a comprehensive view of business operations, enhancing analysis and strategic planning.
Key features:
-
-
-
-
- ETL and ELT capabilities to process and integrate diverse data (using platforms like Actian Data Platform or Informatica).
- Support for multiple data formats and sources, enhancing data accessibility (capabilities seen in Actian Data Platform or SAP Data Warehouse Cloud).
- Data quality tools that clean and validate data (like tools provided by Dataiku).
9. (Facilitates) Business Intelligence: Data warehouses support complex data queries and are integral in generating insightful reports and dashboards, which are crucial for making informed business decisions. Consider this the grand finale where all your data prep work pays off—transforming raw numbers into visual stories that even the most data-phobic executive can understand.
Key features:
-
-
-
-
- Integration with leading BI tools for real-time analytics and reporting (like Tableau).
- Data visualization tools and dashboard capabilities to present actionable insights (such as those in Snowflake and Power BI).
- Advanced query optimization for fast and efficient data retrieval (using technologies like SQL Server Analysis Services).
The technical capabilities we’ve discussed showcase how modern data warehouses are breaking down silos and bridging gaps across organizations. They’re not just tech tools; they’re catalysts for business transformation. In a world where data is the new currency, a well-implemented data warehouse can be your organization’s most valuable investment.
However, as data warehouses grow in power and complexity, many organizations find themselves grappling with a new challenge: managing an increasingly intricate data ecosystem. Multiple vendors, disparate systems, and complex data pipelines can turn what should be a transformative asset into a resource-draining headache.
“In today’s data-driven world, companies need a unified solution that simplifies their data operations. Actian Data Platform offers an all-in-one approach, combining data integration, data quality, and data warehousing, eliminating the need for multiple vendors and complex data pipelines.”
This is where Actian Data Platform shines, offering an all-in-one solution that combines data integration, data quality, and data warehousing capabilities. By unifying these core data processes into a single, cohesive platform, Actian eliminates the need for multiple vendors and simplifies data operations. Organizations can now focus on what truly matters—leveraging data for strategic insights and decision-making, rather than getting bogged down in managing complex data infrastructure.
As we look to the future, the organizations that will thrive are those that can most effectively turn data into actionable insights. With solutions like Actian Data Platform, businesses can truly capitalize on their data warehouse investment, driving meaningful transformation without the traditional complexities of data management.
Experience the data platform for yourself with a custom demo.
About Fenil Dedhia
Fenil Dedhia leads Product Management for Actian's Cloud Portfolio. He has previously guided two startups to success as a PM, excelling at transforming ideas into flagship products that solve complex business challenges. His user-centric, first-principles approach drives innovation across AI and data platform products. Through his Actian blog posts, Fenil explores AI, data governance, and data management topics. Check out his latest insights on how modern data platforms drive business value.