Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics
What is Data Governance?
The Role of Data Governance and Common Use Cases
What is Data Compliance?
The Role of Data Compliance and Common Use Cases
7 Key Differences: Data Governance vs. Data Compliance
How Does Data Governance Help With Data Compliance?
Summing It All Up
Data governance and compliance are terms often used interchangeably, but they serve fundamentally different purposes in your organization’s data strategy. While compliance focuses on meeting specific regulatory requirements, governance encompasses a broader strategic framework that includes compliance as one of its key outcomes.
Think of data governance as your organization’s internal playbook for managing data effectively, while data compliance is about meeting external rules set by regulators and industry standards. In fact, compliance requirements often represent just a subset of the controls and policies that a robust governance framework puts in place.
The main difference? Data governance is always proactive—you create internal frameworks and policies that dictate how your organization handles data. Data compliance requires proactive planning too, but because regulations continuously evolve and new ones emerge, organizations must remain responsive to changing external requirements. Even with established regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) as a foundation, compliance practices need to adapt as interpretations change and new standards develop.
Here’s the key: data compliance is actually an outcome of good data governance, not a separate process. While some platforms position themselves as end-to-end governance solutions, organizations often find more success by starting with focused compliance objectives and gradually expanding their governance capabilities over time. This allows teams to demonstrate quick wins through compliance achievements while building the foundation for broader governance initiatives at a pace that matches their organizational readiness.
“Data governance without compliance is ineffective; compliance without governance is impossible. They’re two sides of the same coin, but governance is the side that determines the coin’s value.”
Understanding the Basics
Before we dive deeper into each concept, let’s establish some clear definitions that will help frame our understanding.
What is Data Governance?
Data governance is a framework that dictates how an organization manages, uses, and protects data assets through internal policies, standards, and controls to ensure compliance, data quality, and security.
Gartner defines data governance as a way to “specify decision rights and accountability to ensure appropriate behavior as organizations seek to value, create, consume, and control their data, analytics, and information assets.”
The Role of Data Governance and Its Use Cases
Data governance is necessary to ensure data is safe, secure, private, usable, and in compliance with external data policies. It establishes controls that enable broader data access while maintaining security and privacy standards.
The main use cases of data governance are as follows:
Data Democratization Oversight: Modern data governance establishes the framework for controlled data sharing across the organization. This involves defining policies for data catalogs, literacy programs, and self-service capabilities that enable teams to access and use data safely while maintaining proper controls.
Data Stewardship: Data governance often means giving accountability and responsibility for both the data itself and the processes that ensure its proper use to “data stewards.” These stewards define standards, create policies, and monitor data quality metrics while facilitating cross-functional collaboration.
Data Quality Control: Data governance establishes the framework and policies for ensuring data quality. This includes defining the standards and metrics across six dimensions:
- Accuracy (correctly representing real-world entities).
- Completeness (all required information is present).
- Consistency (same values across systems).
- Timeliness (available when needed).
- Validity (conforming to business rules).
- Uniqueness (free from unintended duplication).
It’s important to grasp that data quality control isn’t just about defining standards—it’s about making them operational. Product teams often struggle with balancing automated quality checks against performance impact, while consultants face the challenge of implementing quality frameworks that scale across different data domains. For instance, what works for customer data quality might not apply to product usage data. The key is implementing flexible quality frameworks that can adapt to different data types while maintaining consistent governance principles.
Access Control and Security: Data governance defines who can access what data, under what circumstances, and how it should be protected. This involves creating policies for data classification, access rights, security protocols, and privacy requirements.
Policy and Standards Setting: Data governance creates the rules and guidelines for how data should be handled throughout its lifecycle. This includes policies for data collection, storage, usage, sharing, retention, and disposal, which data management then implements.
Modern policy setting must align with agile development practices and DevOps culture. Rather than creating rigid policies that slow down innovation, successful governance frameworks provide guardrails that enable self-service while maintaining control. This might mean implementing policy-as-code, creating automated compliance checks in CI/CD pipelines, and designing data contracts that evolve with your products.
What is Data Compliance?
Data compliance is adherence to external regulations and standards for data privacy and security (like GDPR, HIPAA).
The Role of Data Compliance and its Use Cases
Data compliance can be seen as an outcome of a solid data governance program. Modern data platforms like the Actian Data Intelligence Platform help you configure compliance-based access policies at scale for your data and metadata.
The main use cases of data compliance are as follows:
Industry-Specific Regulatory Compliance: Financial services, healthcare, and education sectors face unique regulatory challenges that demand rigorous data handling practices. These regulations often require organizations to demonstrate not just compliance, but also the mechanisms and controls in place to maintain it.
- Example: A Seattle-based healthcare provider faced HIPAA compliance challenges when transitioning to telehealth in 2020. It needed to demonstrate not just secure video consultations, but also prove compliant storage of patient records, audit trails of data access, and proper encryption of data at rest and in transit.
Privacy Regulation Compliance: The global landscape of privacy regulations continues to evolve, with new frameworks emerging regularly. Organizations must navigate an increasingly complex web of requirements, often needing to comply with multiple jurisdictions simultaneously.
- Example: In January 2024, France’s privacy watchdog CNIL fined Amazon France Logistique €32 million for what it deemed an “excessively intrusive” employee surveillance system. The regulator found issues with how the company tracked employee scanner inactivity time and item scanning speeds, along with retaining this data for extended periods. This case demonstrates how compliance extends beyond customer data privacy to encompass employee privacy rights as well.
Data Security Controls and Protection: Modern compliance frameworks increasingly focus on demonstrable security controls rather than mere policy documents. Organizations must implement and verify technical controls that protect sensitive data throughout its lifecycle.
- Example: A multinational insurance company discovered unauthorized access to 30,000 customer records through a third-party vendor’s compromised credentials. Despite having a substantial security budget, the company faced regulatory penalties because its data wasn’t properly segmented and encrypted. The incident highlighted that compliance requires layered security controls, not just investment in perimeter security.
With the rise of microservices, cloud-native applications, and distributed systems, security controls must evolve beyond traditional perimeter-based approaches. This means implementing security controls at the data level, ensuring that protection travels with the data regardless of where it resides or how it’s accessed. For software companies, this often means rethinking how data flows between services, managing secrets in configuration, and implementing fine-grained access controls at the API level.
Audit and Reporting Requirements: Compliance often requires organizations to maintain detailed audit trails and generate reports demonstrating adherence to regulations. This includes documenting data access patterns, changes to sensitive information, and proof of required security controls.
Cross-Border Data Transfer Compliance: With global operations becoming the norm, organizations must navigate complex requirements for international data transfers. This includes understanding and implementing appropriate data transfer mechanisms, maintaining required documentation, and ensuring continued compliance as regulations evolve.
For software companies, cross-border data transfer compliance presents unique challenges, particularly in product development and customer support scenarios. Consider a typical SaaS application: development teams in multiple countries need access to production data for debugging, while support teams require customer data access across time zones. This requires implementing sophisticated data access patterns that can dynamically adjust based on user location and role, while maintaining compliance with regulations like GDPR’s data transfer requirements.
“Think of data governance as building a house: you need a solid foundation, clear blueprints, and proper construction. Compliance is like the building code inspector – they don’t tell you how to build, they just ensure you’ve met the minimum standards.”
7 Key Differences: Data Governance vs. Data Compliance
1. Strategic Focus
- Data Governance: Internal framework and strategy focused on managing data as a business asset
- Data Compliance: External requirements and regulations that must be followed
2. Core Definition and Purpose
- Data Governance: Framework that dictates how an organization manages, uses, and protects data assets through internal policies, standards, and controls to ensure compliance, data quality, and security
- Data Compliance: Adherence to external regulations and standards for data privacy, security, and handling (like GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA)
3. Primary Goal
- Data Governance: Manage, maintain, and use data to create business value by ensuring your data is accurate, consistent, available, and secure
- Data Compliance: Mitigate legal and regulatory risks associated with data by governing the collection, storage, processing, and sharing of data
4. Scope of Application
- Data Governance: Applies to all organizations seeking to manage their data assets effectively, regardless of size or industry
- Data Compliance: Specific to organizations based on jurisdiction, industry sector, or type of data handled
5. Core Activities
- Data Governance:
- Implementing data classification and tagging frameworks.
- Building data quality control mechanisms and data quality metrics.
- Creating and maintaining data catalogs and metadata.
- Setting up access control hierarchies.
- Developing data integration and interoperability standards.
- Managing data lifecycle from creation to archival.
- Implementing data literacy programs.
- Building data stewardship programs.
- Orchestrating controlled data democratization initiatives.
- Data Compliance:
- Conducting regular/periodic compliance audits and assessments.
- Implementing required security controls and monitoring.
- Maintaining compliance documentation and evidence.
- Delivering compliance training and awareness programs.
- Monitoring regulatory changes and updating procedures.
- Managing data privacy impact assessments.
- Reporting to regulatory bodies as required.
- Responding to compliance incidents and breaches.
- Ensuring vendor and third-party compliance.
6. Interdependency
- Data Governance: Provides the framework and controls that enable compliance.
- Data Compliance: Influences governance policies and procedures to ensure regulatory requirements are met.
7. Key Stakeholders
- Data Governance:
- Chief Data Officer (CDO): Executive leader who drives organization-wide data strategy and oversees data operations.
- Chief Information Officer (CIO): Oversees all IT strategy and ensures alignment between technology and business objectives.
- Data Stewards: Subject matter experts maintaining data quality and metadata.
- Data Governance Manager: Orchestrates governance implementation and ensures stakeholder alignment.
- Data Quality Managers: Lead initiatives to maintain and improve data quality across the organization.
- Data Owners: Business leaders accountable for specific data assets.
- Data Custodians: Technical specialists implementing governance systems.
- Data Product Managers: Oversee development and management of data products and services.
- Domain Owners (Data Mesh Champions): Govern data products while ensuring local autonomy and cross-domain standards compliance.
- Database Administrators: Manage and optimize database systems, ensuring data availability and performance.
- Data Infrastructure Managers: Oversee technical infrastructure (including SRE, IT Ops, DevOps teams).
- Enterprise Architects: Design and oversee the organization’s overall technical and data architecture.
- Data Steering Committee: Cross-functional team setting strategic direction.
- Data Compliance:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): Leads overall information security strategy and risk management.
- Data Protection Officer (DPO): Oversees data protection strategy and GDPR compliance.
- Data Compliance Managers: Ensure adherence to data-related regulations and standards.
- Chief Compliance Officer: Ensures organization-wide regulatory compliance.
- Legal Teams: Interpret regulations and provide legal guidance.
- Information Security Officers: Implement security controls and monitor threats.
- Privacy Specialists: Focus on privacy requirements and implementation.
- Compliance Analysts: Monitor compliance metrics and prepare reports.
- Audit Teams: Conduct internal compliance audits.
- Risk Management Teams: Assess and mitigate data-related risks.
- Training Specialists: Develop compliance training programs.
- External Auditors: Provide independent compliance verification.
“The most successful organizations don’t treat compliance as a checkbox exercise. They build it into their data DNA through strong governance practices, making compliance a natural outcome rather than a forced effort.”
How Does Data Governance Help With Data Compliance?
Data governance serves as the backbone that enables effective data compliance by providing the structure, processes, and controls needed to meet regulatory requirements. Here’s how data governance specifically supports compliance objectives:
1. Foundational Infrastructure
- Provides the technical and organizational framework required to implement compliance controls.
- Creates clear data classification schemes that help identify regulated data.
- Establishes data lineage tracking that demonstrates regulatory conformity.
- Maintains comprehensive data inventories needed for compliance reporting.
2. Policy Implementation
- Translates regulatory requirements into actionable internal policies.
- Creates standardized procedures for handling sensitive data.
- Ensures consistent application of compliance controls across the organization.
- Enables systematic policy updates as regulations evolve.
3. Access Control and Security
- Implements role-based access control aligned with compliance requirements.
- Maintains audit trails of data access and usage.
- Enforces data protection measures required by regulations.
- Provides mechanisms for data masking and encryption.
4. Documentation and Evidence
- Maintains detailed records of data handling practices.
- Creates audit trails for compliance verification.
- Provides evidence of policy enforcement.
- Supports regulatory reporting requirements.
5. Risk Management
- Identifies potential compliance risks through data monitoring.
- Enables proactive mitigation of compliance issues.
- Provides early warning of potential violations.
- Supports incident response and remediation.
The synergy between governance and compliance creates a virtuous cycle: strong governance makes compliance more achievable, while compliance requirements help strengthen governance practices. This relationship is essential for organizations seeking to both protect their data assets and meet their regulatory obligations.
Summing It All Up
Understanding the relationship between data governance, data management, and data compliance is crucial for building an effective data strategy. While these concepts are interconnected, they serve distinct purposes:
- Data governance provides the internal framework and rules—your organization’s playbook for handling data assets. It’s proactive, setting the standards and controls that guide how data should be managed, used, and protected.
- Data management puts these rules into action through day-to-day operations, tools, and processes. It’s the execution arm that implements the governance framework’s requirements.
- Data compliance validates your practices against external regulations. While governance creates the internal rules and management executes them, compliance ensures these align with external requirements like GDPR or HIPAA.
Think of it as a three-part system: governance creates the playbook, management runs the plays, and compliance keeps score against external standards. When these three components work in harmony, organizations can both protect and maximize the value of their data assets.
As data landscapes grow more complex and regulations more stringent, organizations face increasing challenges in maintaining effective governance while ensuring compliance. Many find themselves struggling with disconnected tools, manual processes, and unclear data lineage—turning what should be strategic assets into operational burdens.
In today’s regulatory environment, organizations need a unified solution that simplifies data governance while ensuring compliance. Actian Data Intelligence Platform bridges the gap between governance and compliance, providing the visibility and control needed to confidently manage data assets.
This is where the platform makes a difference.
Actian Data Intelligence Platform for Data Governance and Compliance
As a modern metadata management and data intelligence platform, Actian’s platform simplifies both data governance and compliance through automation and federation:
For governance, the Actian Data Intelligence Platform delivers:
- Federated data governance that supports decentralized models like data mesh, enabling local autonomy while maintaining enterprise-wide oversight.
- Automated data lineage and documentation that shows where data comes from, how it changes, and who owns it—building data trust while reducing risk.
- Streamlined governance through automated metadata discovery, classification, and AI-powered data stewardship recommendations.
Unlike traditional platforms that rely on rigid, centralized approaches and manual stewardship, Actian’s modern architecture enables automated, federated governance that works seamlessly across multi-cloud and hybrid environments without vendor lock-in.
For compliance, the Actian Data Intelligence Platform provides:
- Automated compliance readiness with dynamic classification and tracking of sensitive data and PII.
- Policy-based access controls that balance self-service with governance.
- Comprehensive audit and regulatory reporting capabilities that track data usage, lineage, and regulatory alignment.
While traditional compliance tools remain static and rule-bound, the Actian Data Intelligence Platform’s lightweight, agile approach enables domain-specific compliance enforcement that aligns with modern data principles—integrating seamlessly without adding friction to existing workflows.
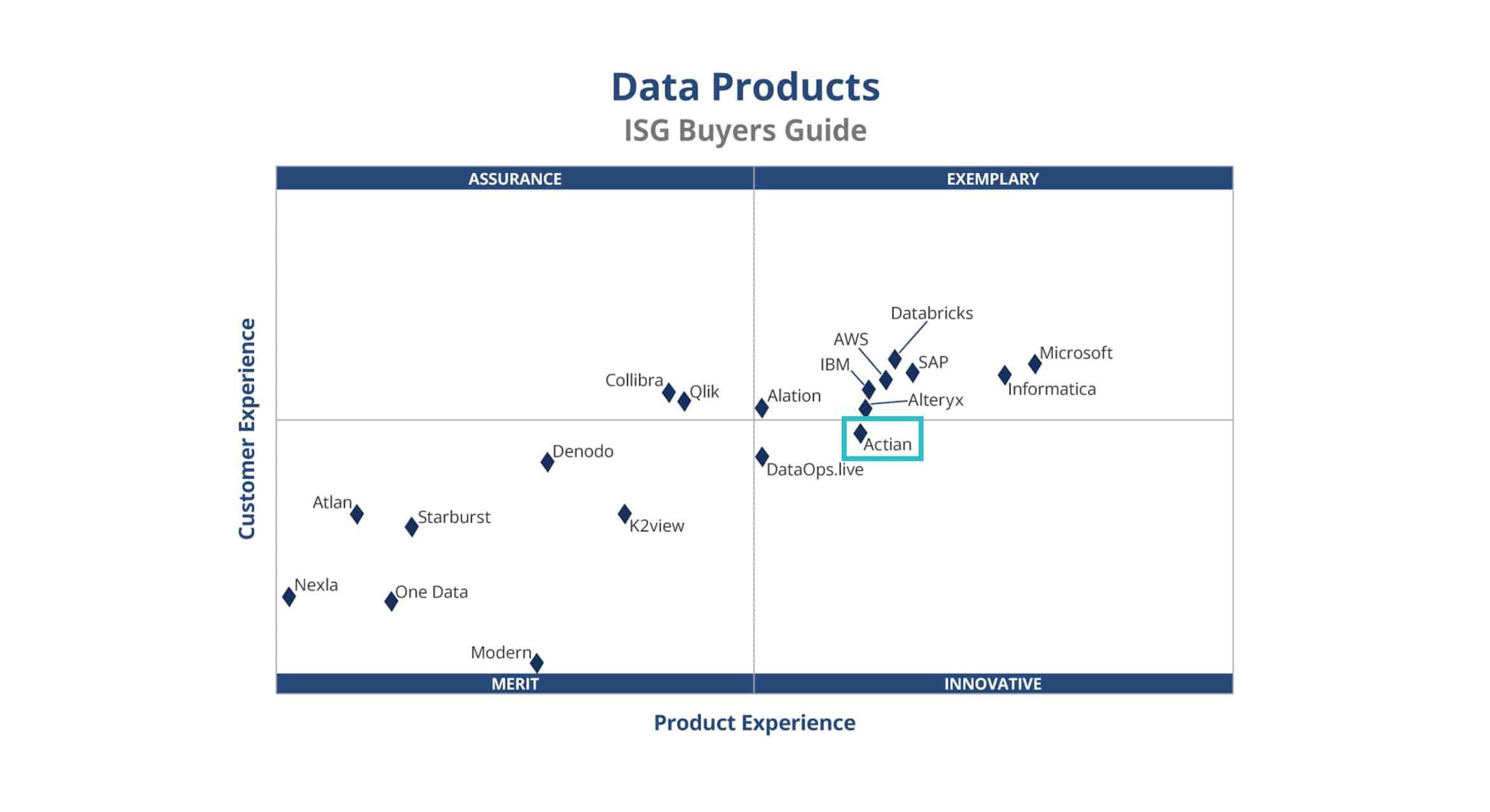
Selecting the ideal data solution requires careful evaluation. The ISG Buyers Guide for Data Products, like the ISG Buyers Guide for Data Platforms, is a trusted, third-party resource for organizations looking to navigate this complex product landscape. For insights into choosing the right products for your business, download your complimentary copy of the ISG Buyers Guide for Data Products. It evaluates 19 vendors based on a comprehensive set of criteria in various categories including product experience, capabilities, reliability, customer experience, return on investment, and more.
Looking ahead, successful organizations will be those that can maintain strong governance while adapting to evolving data terminology and compliance requirements. With platforms like the Actian Data Intelligence Platform, businesses can transform their data governance from a compliance burden into a strategic advantage, focusing on creating value rather than just managing risk.
About Fenil Dedhia
Fenil Dedhia leads Product Management for Actian's Cloud Portfolio. He has previously guided two startups to success as a PM, excelling at transforming ideas into flagship products that solve complex business challenges. His user-centric, first-principles approach drives innovation across AI and data platform products. Through his Actian blog posts, Fenil explores AI, data governance, and data management topics. Check out his latest insights on how modern data platforms drive business value.