AI Observability: What it is and How it Works
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) becomes a cornerstone of digital transformation across industries, it’s crucial to ensure its reliability, transparency, and performance. AI observability is a rising discipline designed to provide insight into the internal workings of AI systems.
It empowers organizations to monitor, debug, and improve AI models and infrastructure in real time, much like how traditional observability helps manage software systems. This article explores what AI observability is, why it matters, its core components, and how businesses can implement it effectively.
Defining AI Observability
AI observability refers to the ability to monitor, understand, and explain the behavior of AI systems across their entire lifecycle—from data ingestion and model training to deployment and real-time inference. It goes beyond simple logging or monitoring by offering holistic visibility into how data, models, and infrastructure interact.
The Role of AI Observability in Modern Systems
In traditional software engineering, observability focuses on metrics, logs, and traces to ensure application health. AI observability builds on this foundation but addresses AI-specific elements such as model drift, data skew, and fairness.
Its role is multifaceted:
- Transparency: Making black-box models more understandable.
- Accountability: Ensuring models perform ethically and within regulatory bounds.
- Optimization: Enhancing system performance and reducing resource waste.
With AI now embedded in mission-critical workflows (for instance, organizations are increasingly using AI for loan approvals, medical diagnoses, and fraud detection), observability isn’t just beneficial; it’s essential.
AI Observability’s Role
Let’s take a closer look at the role of AI observability within a larger organization. Below, we discuss some simple benefits that come from a consistent data observability program.
Enhancing System Reliability
AI systems are notoriously complex and sensitive to changing inputs, environments, and user behavior. AI observability enhances reliability by continuously tracking key indicators like:
- Model accuracy and latency.
- Input/output data trends.
- Infrastructure availability.
This ensures that the AI system performs consistently, even in dynamic conditions.
Facilitating Proactive Issue Resolution
Rather than reacting to failures after they occur, observability allows teams to anticipate issues. For example, a spike in prediction latency or a drop in confidence scores can signal impending failure. Observability tools can trigger alerts, identify root causes, and even suggest fixes before customers or end-users are impacted.
Key Components of AI Observability
AI observability consists of several components. First, we will discuss the cycle of AI observability and then list a few ways in which a proper observability program can help organizations improve and maintain high data quality.
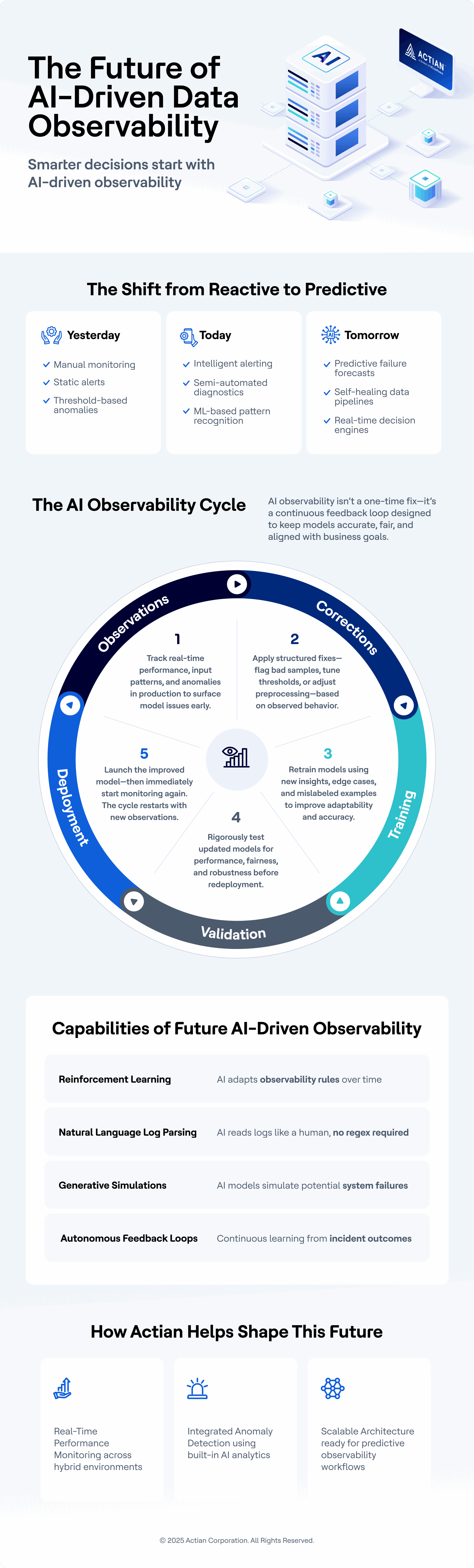
The AI Observability Cycle: From Observations to Deployment
AI observability is a continuous, iterative process that ensures models remain accurate, fair, and aligned with business goals. This process typically follows a cycle consisting of observations, corrections, training, validation, and deployment:
- Observations
Observability begins with capturing real-time insights into model behavior in production. This includes tracking performance metrics, analyzing input distributions, and detecting anomalies or failure patterns. These observations provide the critical data needed to understand how a model is functioning in the wild. - Corrections
Once issues are observed, teams can apply targeted corrections. This might involve flagging problematic samples, adjusting decision thresholds, or updating preprocessing pipelines. Corrections are not always immediate model changes but rather structured inputs into the improvement process. - Training
Corrected insights inform the next training cycle. New or updated data, including edge cases and previously misclassified examples, are used to retrain the model. This step ensures the model learns from its mistakes and adapts to new patterns or distributions. - Validation
Before deployment, retrained models must be rigorously validated. This includes not only standard metrics but also robustness checks, fairness audits, and performance evaluations under various conditions. Validation ensures that changes improve the model without introducing new risks. - Deployment
Once validated, the improved model is deployed into production. However, this doesn’t mark the end of the cycle. Instead, observability tools immediately begin collecting new data and metrics, restarting the loop at the “Observations” step. This continuous deployment-feedback cycle enables sustained model performance and trustworthiness over time.
Metrics Used in AI Observability
Beyond standard metrics like accuracy or precision, AI observability dives deeper. It includes factors like:
- Drift detection (e.g., concept and data drift).
- Fairness and bias checks.
- Confidence interval analysis.
These insights enable continuous evaluation and retraining of models, helping prevent deterioration over time.
System Resource Management
AI systems demand substantial computational resources. Observability also involves checking and managing resource usage, including:
- GPU/CPU utilization.
- Memory bottlenecks.
- Throughput per node or container.
Monitoring system resources ensures AI workloads are optimized and cost-effective.
Challenges in Implementing AI Observability
Implementing any systematic observability program will involve some challenges, despite the numerous benefits. Below, we’ve listed some of the more common issues organizations might face when putting a robust AI observability process in place.
Overcoming Data Complexity
AI models rely on diverse and high-dimensional data. Observing data pipelines that involve real-time streams, batch processing, and third-party sources is a complex ask. Organizations must design observability solutions that can handle:
- Unstructured data (e.g., images, text).
- Multi-modal inputs.
- Large-scale feature sets.
Solving this requires scalable data tracking systems and robust validation mechanisms.
Ensuring Scalability and Flexibility
As organizations deploy AI across more business units and use cases, observability systems must scale accordingly. This includes:
- Supporting cloud-native, hybrid, and on-prem environments.
- Integrating with multiple AI frameworks (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch).
- Handling high-throughput data pipelines.
Scalability must also be matched with flexibility to support experimentation and model updates without disrupting observability.
How to Get Started With AI Observability
Here are the six steps to take when first implementing an AI observability process within an organization.
- Define objectives: Understand what the organization wants to observe. This could include data drift, model bias, resource usage, etc.
- Audit the current AI stack: Identify gaps in visibility across data, models, and infrastructure.
- Select observability tools: Choose solutions that align with the chosen use cases and integrate well with existing data pipelines.
- Start with pilot projects: Monitor a single AI system, gather feedback, and iterate across additional projects. This can help identify problems in the process before they affect things on a larger scale.
- Automate and scale: Once successful, apply observability practices across other models and systems.
- Create a governance framework: Assign roles, responsibilities, and SLAs for maintaining observability.
Tools and Technologies to Consider
Here are key tools for AI observability categorized by functionality:
- Model Monitoring: Arize AI, Fiddler, Superwise, WhyLabs.
- Pipeline Orchestration: Airflow, Kubeflow, Prefect.
- Versioning & Experiment Tracking: MLflow, DVC, Weights & Biases.
- Data Validation: Great Expectations, Evidently AI.
- Infrastructure Monitoring: Prometheus, Grafana, Datadog.
Choosing the right combination ensures that all layers of the AI stack (data, model, and infrastructure) are continuously observable.
Actian: At the Forefront of AI Observability Trends
Actian is a leader in hybrid data analytics and is actively shaping the future of AI observability.
Here’s how the Actian Data Intelligence Platform supports AI observability:
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Ensures AI systems receive fresh, reliable data through built-in validation and cleansing.
- Integrated Model Observability: Seamlessly connects model outputs with operational dashboards and alerts.
- Cross-System Integration: Bridges AI workloads across cloud and on-prem environments, offering visibility into the full data journey.
- Scalable Data Architecture: Supports large-scale AI deployments without compromising performance or control.
With Actian, organizations gain the infrastructure and tools needed to monitor AI pipelines, respond proactively to issues, and ensure models deliver consistent, trustworthy results.