Data Observability vs. Data Monitoring

Two pivotal concepts have emerged at the forefront of modern data infrastructure management, both aimed at protecting the integrity of datasets and data pipelines: data observability and data monitoring. While they may sound similar, these practices differ in their objectives, execution, and impact. Understanding their distinctions, as well as how they complement each other, can empower teams to make informed decisions, detect issues faster, and improve overall data trustworthiness.
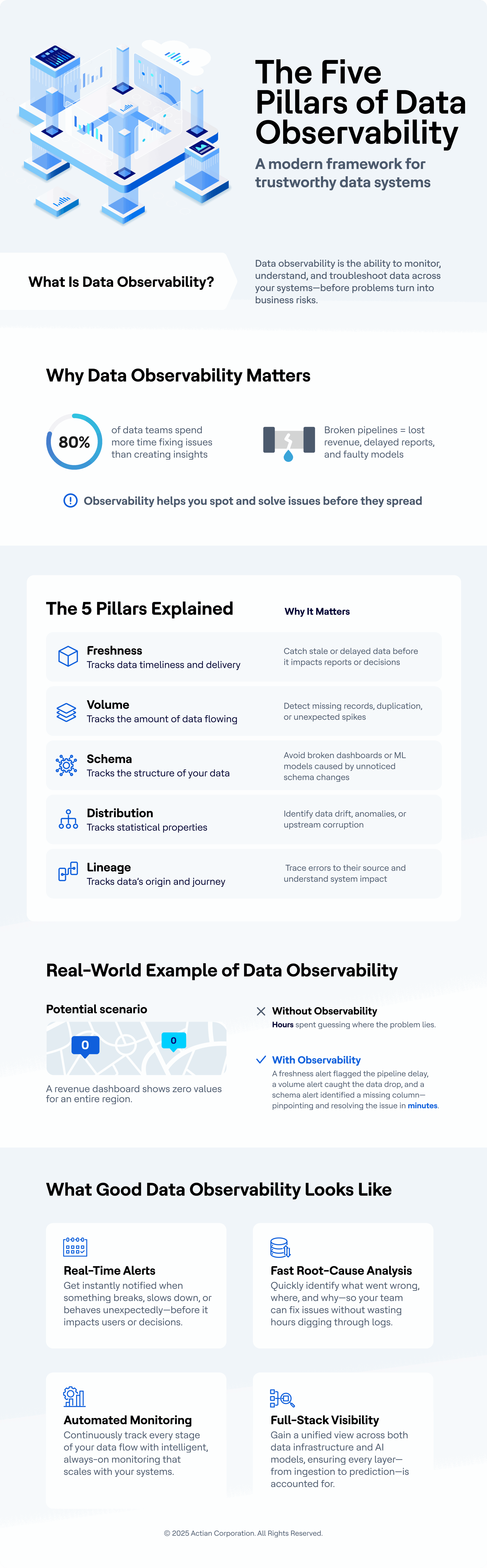
What is Data Observability?
Data Observability is the practice of understanding and monitoring data’s behavior, quality, and performance as it flows through a system. It provides insights into data quality, lineage, performance, and reliability, enabling teams to detect and resolve issues proactively.
Components of Data Observability
Data observability comprises five key pillars, which answer five key questions about datasets.
- Freshness: Is the data up to date?
- Volume: Is the expected amount of data present?
- Schema: Have there been any unexpected changes to the data structure?
- Lineage: Where does the data come from, and how does it flow across systems?
- Distribution: Are data values within expected ranges and formats?
These pillars allow teams to gain end-to-end visibility across pipelines, supporting proactive incident detection and root cause analysis.
Benefits of Implementing Data Observability
- Proactive Issue Detection: Spot anomalies before they affect downstream analytics or decision-making.
- Reduced Downtime: Quickly identify and resolve data pipeline issues, minimizing business disruption.
- Improved Trust in Data: Enhanced transparency and accountability increase stakeholders’ confidence in data assets.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation of anomaly detection reduces manual data validation.
What is Data Monitoring?
Data monitoring involves the continuous tracking of data and systems to identify errors, anomalies, or performance issues. It typically includes setting up alerts, dashboards, and metrics to oversee system operations and ensure data flows as expected.
Components of Data Monitoring
Core elements of data monitoring include the following.
- Threshold Alerts: Notifications triggered when data deviates from expected norms.
- Dashboards: Visual interfaces showing system performance and data health metrics.
- Log Collection: Capturing event logs to track errors and system behavior.
- Metrics Tracking: Monitoring KPIs such as latency, uptime, and throughput.
Monitoring tools are commonly used to catch operational failures or data issues after they occur.
Benefits of Data Monitoring
- Real-Time Awareness: Teams are notified immediately when something goes wrong.
- Improved SLA Management: Ensures systems meet service-level agreements by tracking uptime and performance.
- Faster Troubleshooting: Log data and metrics help pinpoint issues.
- Baseline Performance Management: Helps maintain and optimize system operations over time.
Key Differences Between Data Observability and Data Monitoring
While related, data observability tools and data monitoring are not interchangeable. They serve different purposes and offer unique value to modern data teams.
Scope and Depth of Analysis
- Monitoring offers a surface-level view based on predefined rules and metrics. It answers questions like, “Is the data pipeline running?”
- Observability goes deeper, allowing teams to understand why an issue occurred and how it affects other parts of the system. It analyzes metadata and system behaviors to provide contextual insights.
Proactive vs. Reactive Approaches
- Monitoring is largely reactive. Alerts are triggered after an incident occurs.
- Observability is proactive, enabling the prediction and prevention of failures through pattern analysis and anomaly detection.
Data Insights and Decision-Making
- Monitoring is typically used for operational awareness and uptime.
- Observability helps drive strategic decisions by identifying long-term trends, data quality issues, and pipeline inefficiencies.
How Data Observability and Monitoring Work Together
Despite their differences, data observability and monitoring are most powerful when used in tandem. Together, they create a comprehensive view of system health and data reliability.
Complementary Roles in Data Management
Monitoring handles alerting and immediate issue recognition, while observability offers deep diagnostics and context. This combination ensures that teams are not only alerted to issues but are also equipped to resolve them effectively.
For example, a data monitoring system might alert a team to a failed ETL job. A data observability platform would then provide lineage and metadata context to show how the failure impacts downstream dashboards and provide insight into what caused the failure in the first place.
Enhancing System Reliability and Performance
When integrated, observability and monitoring ensure:
- Faster MTTR (Mean Time to Resolution).
- Reduced false positives.
- More resilient pipelines.
- Clear accountability for data errors.
Organizations can shift from firefighting data problems to implementing long-term fixes and improvements.
Choosing the Right Strategy for An Organization
An organization’s approach to data health should align with business objectives, team structure, and available resources. A thoughtful strategy ensures long-term success.
Assessing Organizational Needs
Start by answering the following questions.
- Is the organization experiencing frequent data pipeline failures?
- Do stakeholders trust the data they use?
- How critical is real-time data delivery to the business?
Organizations with complex data flows, strict compliance requirements, or customer-facing analytics need robust observability. Smaller teams may start with monitoring and scale up.
Evaluating Tools and Technologies
Tools for data monitoring include:
- Prometheus
- Grafana
- Datadog
Popular data observability platforms include:
- Monte Carlo
- Actian Data Intelligence Platform
- Bigeye
Consider ease of integration, scalability, and the ability to customize alerts or data models when selecting a platform.
Implementing a Balanced Approach
A phased strategy often works best:
- Establish Monitoring First. Track uptime, failures, and thresholds.
- Introduce Observability. Add deeper diagnostics like data lineage tracking, quality checks, and schema drift detection.
- Train Teams. Ensure teams understand how to interpret both alert-driven and context-rich insights.
Use Actian to Enhance Data Observability and Data Monitoring
Data observability and data monitoring are both essential to ensuring data reliability, but they serve distinct functions. Monitoring offers immediate alerts and performance tracking, while observability provides in-depth insight into data systems’ behavior. Using both concepts together with the tools and solutions provided by Actian, organizations can create a resilient, trustworthy, and efficient data ecosystem that supports both operational excellence and strategic growth.
Actian offers a suite of solutions that help businesses modernize their data infrastructure while gaining full visibility and control over their data systems.
With the Actian Data Intelligence Platform, organizations can:
- Monitor Data Pipelines in Real-Time. Track performance metrics, latency, and failures across hybrid and cloud environments.
- Gain Deep Observability. Leverage built-in tools for data lineage, anomaly detection, schema change alerts, and freshness tracking.
- Simplify Integration. Seamlessly connect to existing data warehouses, ETL tools, and BI platforms.
- Automate Quality Checks. Establish rule-based and AI-driven checks for consistent data reliability.
Organizations using Actian benefit from increased system reliability, reduced downtime, and greater trust in their analytics. Whether through building data lakes, powering real-time analytics, or managing compliance, Actian empowers data teams with the tools they need to succeed.