Data Observability Tools

As organizations process massive volumes of data across distributed systems, the risks of data degradation, downtime, and inaccurate analytics have grown substantially. This is where data observability tools become increasingly important. These tools provide end-to-end visibility into data infrastructure, enabling teams to detect, diagnose, and resolve data issues early, before they move downstream.
This article explores what data observability is, the features of leading tools, how to choose the right solution, and how providers like Actian are helping organizations achieve robust data observability.
What is Data Observability?
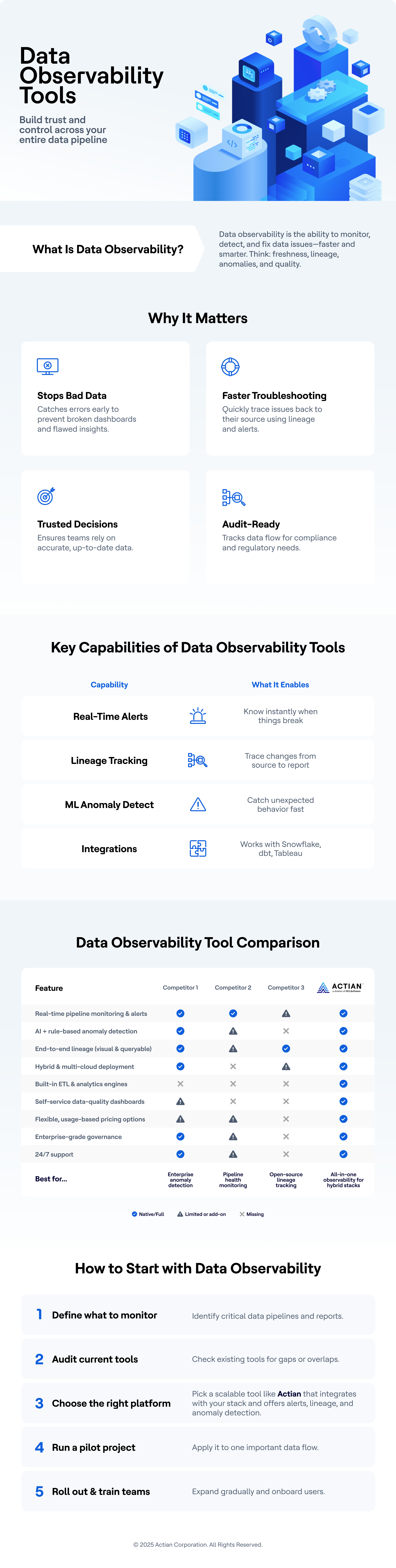
Data observability refers to an organization’s ability to monitor, understand, and trust the data flowing through its systems. It borrows from the principles of software observability—metrics, logs, and traces—but adapts them for the unique challenges of data infrastructure.
Rather than only monitoring performance metrics, data observability tools offer a deeper layer of insight into data quality, lineage, dependencies, freshness, and anomalies across complex environments.
Why Data Observability is Critically Important
As modern data stacks grow more fragmented, it becomes harder to trace data issues. As a result, a delay in a single upstream source or a transformation error in a data pipeline can cascade into analytics dashboards, causing flawed business decisions. Without observability, identifying and resolving such issues is difficult and time-consuming.
Data observability ensures:
- Real-time detection of data issues.
- Reduced data downtime.
- Better collaboration between data teams.
- More accurate, trusted, and timely analytics.
It’s essential for maintaining trust in data products and minimizing business risk.
Key Benefits of Implementing Data Observability
Organizations that use a data observability solution can realize benefits that span:
- Improved Data Quality: Proactively spot and fix errors.
- Faster Root Cause Analysis: Trace issues back to their source with data lineage.
- Optimized Operations: Automate alerting and reduce the need for manual checks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Track how data is transformed and where it travels.
- Greater Trust in Data: Equip decision-makers with reliable data and insights.
Core Features of Data Observability Tools
Data observability tools differ in their approaches and capabilities. However, there are core features that any good observability tool should include, such as the following:
Monitoring and Alerting Capabilities
At the heart of any data observability tool is real-time monitoring and intelligent alerting. These features allow data teams to:
- Monitor pipeline health and data freshness.
- Detect schema changes or anomalies.
- Receive alerts when thresholds are crossed.
These capabilities prevent downstream users from working with stale or incorrect data.
Data Lineage and Impact Analysis
Data lineage tracks the journey of data from source to destination, documenting how it changes along the way. Impact analysis lets organizations understand how changes to upstream systems might affect downstream uses. Together, data lineage and analysis provide:
- Full visibility into dependencies.
- Faster troubleshooting.
- Enhanced compliance reporting.
Lineage diagrams also support audit trails for governance and regulatory needs.
Integration With Existing Data Systems
Effective data observability tools integrate seamlessly with:
- Data warehouses (BigQuery, Redshift).
- ETL/ELT tools (Fivetran, dbt, Airflow).
- BI tools (Tableau, Looker, Power BI).
- Cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
This integration ensures complete visibility across the data stack, without the need to overhaul existing systems.
Choosing the Right Data Observability Tool
When selecting a solution, decision makers should focus on core capabilities such as:
- Anomaly detection.
- Root cause analysis.
- Automated documentation.
- Custom alert configuration.
- Scalability across large datasets.
Organizations should look for tools that use machine learning to provide contextual insights, rather than static thresholds alone.
Assessing Compatibility With Current Infrastructure
The chosen observability tool should complement, not complicate, the organization’s current setup. Key compatibility considerations include:
- Supported data sources and destinations.
- Native integration with orchestration tools.
- Deployment options (SaaS vs. on-premises).
- API access and extensibility.
Choosing a tool that aligns with the existing architecture accelerates time to value and reduces implementation friction.
Considering Scalability and Future Needs
As an organization grows, so will its data infrastructure. Any observability solution should scale to accommodate:
- Increased data volume and velocity.
- More diverse data types (structured, semi-structured, unstructured).
- Cross-cloud and hybrid environments.
Tools that offer flexible deployment models and modular pricing can scale cost-effectively with evolving needs.
Data Observability vs. Data Monitoring
Although sometimes used interchangeably, data observability and data monitoring are not precisely the same.
| Feature | Data Monitoring | Data Observability |
| Focus | Surface-level metrics (latency, load) | Deep visibility into data state and health |
| Scope | Infrastructure performance | Data quality, lineage, and transformations |
| Problem Detection | Reactive | Proactive and predictive |
| Tooling | Often limited to logs and dashboards | Uses machine learning, anomaly detection, and lineage |
While monitoring is necessary, observability is comprehensive and offers the full picture. Data monitoring can be seen as a subset of a more complex data observability framework.
When to Use Each Approach
- Data monitoring is suitable for tracking system health and performance metrics.
- Data observability is ideal when organizations need a detailed understanding of how data is moving, transforming, and impacting business decisions.
In practice, organizations benefit the most by using both in tandem.
Implementing Data Observability
Below are steps to implement data observability frameworks as well as solve common challenges organizations typically face.
6 Steps to Successful Implementation
- Define objectives: Identify which data systems and pipelines need observability.
- Audit existing tools: Understand what observability capabilities are already in place.
- Select a pilot project: Start small with a critical data flow or reporting system.
- Choose a tool: Select a solution that integrates with the data stack and supports the defined objectives or goals.
- Roll out incrementally: Scale observability across systems and refine observability based on early learnings.
- Train teams: Ensure analysts, engineers, and data stewards understand how to use the solution and can respond to observability insights.
Overcoming Common Challenges
- Culture change: Resistance to adopting new tools or workflows can be a hurdle. Foster a culture of data ownership and accountability.
- Complexity: Start with foundational metrics, then layer on advanced features like data lineage or machine learning-based anomaly detection.
- Tool fatigue: Avoid overlapping tools by selecting a comprehensive observability solution that covers multiple needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Check out these concise answers to the most commonly asked questions regarding data observability tools.
How do data observability tools improve data quality?
They provide real-time insights into data issues such as:
- Missing values.
- Unexpected schema changes.
- Outliers or anomalies.
By alerting teams early and tracing issues to their origin, observability tools help maintain data accuracy and completeness.
Can data observability tools reduce operational costs?
Yes. By automating data checks and reducing manual monitoring efforts, these tools:
- Lower downtime and incident response times.
- Improve operational efficiency.
- Help prevent costly business decisions based on flawed data.
The return on investment comes from fewer errors, faster root cause analysis, and reduced reliance on human oversight.
What are the risks of not using data observability tools?
Without observability, organizations risk:
- Using incorrect or outdated data.
- Losing trust in dashboards and reports.
- Violating regulatory requirements.
- Wasting time on reactive firefighting.
- Experiencing data quality issues cascading downstream.
Manual data observability with minimal to no tools is unfeasible as organizations scale. Without tools that automate the process, teams risk losing time on manual labor, missing data problems entirely, or being unable to track problems back to their root causes.
These risks compound as data ecosystems grow.
How Actian Empowers Organizations With Data Observability
Actian is a trusted leader in data integration and hybrid data analytics. With solutions like the Actian Data Intelligence Platform, Actian empowers organizations to build robust, trusted, observable data pipelines.
Actian supports observability through:
- Real-time monitoring of data pipelines and ETL jobs.
- Data validation and anomaly detection at every stage.
- Comprehensive data lineage and impact analysis.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud compatibility.
Ready to see how the platform can help organizations maintain and improve data observability? Sign up for a personalized demo today.