Achieve BCBS 239 compliance with confidence
Ensure fast, accurate, and complete risk data aggregation and reporting with Actian’s trusted data solutions.
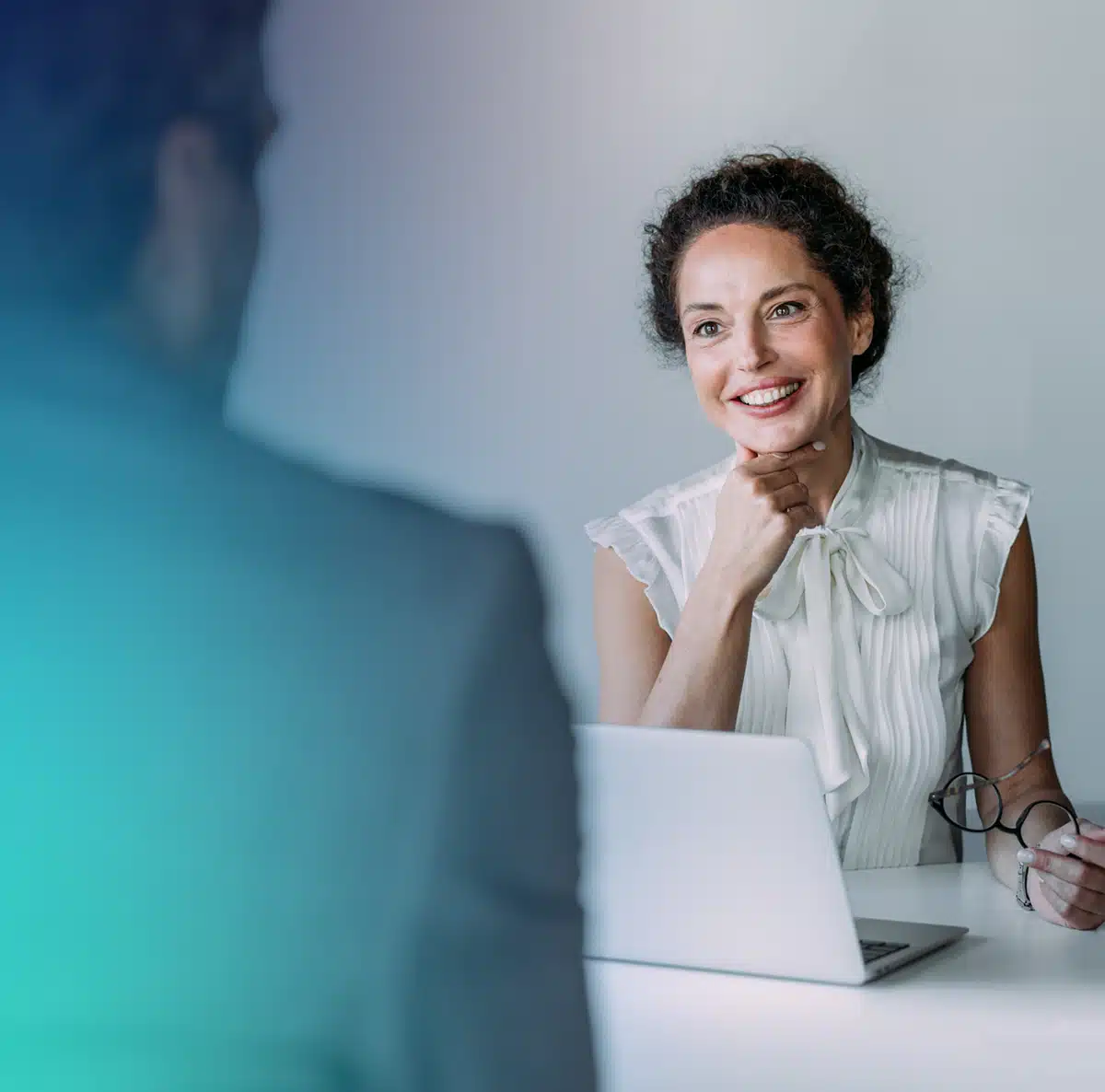







What is BCBS 239 and why does it matter?
BCBS 239 is a global regulatory framework aimed at strengthening banks’ risk data aggregation and risk reporting. It applies to Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs) and sets the benchmark for how financial institutions manage data during periods of stress.
Understanding the 14 BCBS 239 principles
These are the foundational principles for managing risk data across the organization.
- Governance: Banks must assign clear responsibilities for risk data aggregation and reporting. Senior leaders should review and approve data frameworks to ensure consistency and accountability.
- Data architecture and IT infrastructure: Banks need IT systems that can handle risk data accurately and consistently– both during normal operations and periods of stress.
Principles focused on collecting, processing, and adapting risk data.
- Accuracy and integrity: All data must be reliable and error-free to minimize risk misjudgments.
- Completeness: Risk data should cover every major risk and business area– nothing should be left out.
- Timeliness: Data must be delivered fast– especially during market volatility.
- Adaptability: Banks should be able to pivot and adjust their data processes to meet evolving reporting needs.
Standards for the accuracy, clarity, and frequency of risk reports.
- Accuracy of risk reporting: Reports must reflect accurate and validated risk data to inform key decisions.
- Comprehensiveness: Reports must address all significant risk types and match the scale of the bank’s operations.
- Clarity and usefulness: Reports should be easy to read and provide actionable insights for senior leaders.
- Frequency: Reporting schedules should align with the risk’s urgency and management needs.
- Distribution: Reports must be shared with the right teams– securely and without delay.
How regulators evaluate compliance and collaborate across borders.
- Review: Regulators must regularly assess how well banks follow BCBS 239 principles.
- Remedial actions: Regulators should enforce corrective measures when data standards fall short.
- Home/Host cooperation: Supervisory bodies across jurisdictions must coordinate to enforce global compliance standards.
Implementation best practices
Implementing BCBS 239 isn’t just about checking boxes– it requires foundational shifts in how banks manage, trace, and report risk data.
Unified metadata catalog and data discovery
When risk data is scattered, it’s difficult to generate unified reports or perform accurate risk aggregation. By centralizing metadata from all sources and offering enterprise-wide visibility, a data intelligence platform allows teams to easily discover, understand, and align risk data for consistent reporting.
Standardized business glossaries and data quality rules
Inconsistent metrics and missing data lead to flawed reporting, eroding trust and falling short of regulatory requirements. Ensure every risk report is complete, consistent, and compliant by standardizing definitions within a business glossary and embedding data quality checks.
Automated, scalable data pipelines
Legacy systems and manual workflows delay the delivery of risk data– especially during high-stress market conditions. A modern data intelligence platform automates risk data aggregation and scales dynamically to meet urgent timelines, ensuring reports are generated quickly and reliably.
End-to-end data lineage mapping
Without transparent data flow tracking, it’s difficult to validate risk data or explain discrepancies during regulatory audits. Interactive lineage tools will map every transformation, movement, and use of risk data– providing audit-ready transparency and full traceability from source to report.
Role-based access and policy-driven governance
When governance is weak or inconsistent, organizations struggle to manage sensitive risk data securely and ensure accountability. A data intelligence platform enforces data ownership, access controls, and usage policies– ensuring regulatory-grade governance and compliance.
Federated compliance views
Multinational banks face fragmented supervision, with varying compliance requirements across countries and regulators. With jurisdiction-specific metadata layers and reporting views, banks can meet local regulations while maintaining global consistency.
Your Essential Data Intelligence Checklist
Whether you’re just starting your compliance journey or optimizing for data strategy, this checklist breaks down the critical components of a successful data intelligence framework– tailored for risk reporting, governance, and regulatory readiness. This is aimed to help you:
- Evaluate your current capabilities.
- Identify data gaps and governance risks.
- Prioritize next steps for compliance and scalability.
- Align teams around a unified data strategy.
Don’t wait to uncover blind spots– get the clarity you need today.







